Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 ambient on threshold voltage stability in 4H-SiC metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors
ambient on threshold voltage stability in 4H-SiC metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistorsHosoi, Takuji*; Osako, Momoe*; Moges, K.*; Ito, Koji*; Kimoto, Tsunenobu*; Sometani, Mitsuru*; Okamoto, Mitsuo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Shimura, Takayoshi*; Watanabe, Heiji*
Applied Physics Express, 15(6), p.061003_1 - 061003_5, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:32.25(Physics, Applied)The combination of NO annealing and subsequent post-nitridation annealing (PNA) in CO ambient for SiO
ambient for SiO /SiC structures has been demonstrated to be effective in obtaining both high channel mobility and superior threshold voltage stability in SiC-based metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFETs). N atoms on the SiO
/SiC structures has been demonstrated to be effective in obtaining both high channel mobility and superior threshold voltage stability in SiC-based metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFETs). N atoms on the SiO side of the SiO
side of the SiO /SiC interface incorporated by NO annealing, which are plausible cause of charge trapping sites, could be selectively removed by CO
/SiC interface incorporated by NO annealing, which are plausible cause of charge trapping sites, could be selectively removed by CO -PNA at 1300
-PNA at 1300 C without oxidizing the SiC. CO
C without oxidizing the SiC. CO -PNA was also effective in compensating oxygen vacancies in SiO
-PNA was also effective in compensating oxygen vacancies in SiO , resulting high immunity against both positive and negative bias-temperature stresses.
, resulting high immunity against both positive and negative bias-temperature stresses.
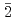 0) MOS devices
0) MOS devicesNakanuma, Takato*; Kobayashi, Takuma*; Hosoi, Takuji*; Sometani, Mitsuru*; Okamoto, Mitsuo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Shimura, Takayoshi*; Watanabe, Heiji*
Applied Physics Express, 15(4), p.041002_1 - 041002_4, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:64.66(Physics, Applied)The leakage current and flat-band voltage (VFB) instability of NO-nitrided SiC (11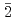 0) (a-face) MOS devices were systematically investigated. Although NO nitridation is effective in improving the interface properties, we found that it reduces the onset field of Fowler-Nordheim (F-N) current by about 1 MVcm
0) (a-face) MOS devices were systematically investigated. Although NO nitridation is effective in improving the interface properties, we found that it reduces the onset field of Fowler-Nordheim (F-N) current by about 1 MVcm , leading to pronounced leakage current. Synchrotron X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy revealed that the nitridation reduces the conduction band offset at the SiO
, leading to pronounced leakage current. Synchrotron X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy revealed that the nitridation reduces the conduction band offset at the SiO /SiC interface, corroborating the above finding. Furthermore, systematical positive and negative bias stress tests clearly indicated the VFB instability of nitrided a-face MOS devices against electron and hole injection.
/SiC interface, corroborating the above finding. Furthermore, systematical positive and negative bias stress tests clearly indicated the VFB instability of nitrided a-face MOS devices against electron and hole injection.
 O vapor on GaN surfaces
O vapor on GaN surfacesSumiya, Masatomo*; Sumita, Masato*; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Sakamoto, Tetsuya; Sang, L.*; Harada, Yoshitomo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 23(1), p.189 - 198, 2022/00
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:48.81(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)GaN is an attracting material for power-electronic devices. Understanding the oxidation at GaN surface is important for improving metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) devices. In this study, the oxidation at GaN surfaces depending on the GaN crystal planes (+c, -c, and m-plane) was investigated by real time XPS and DFT-MD simulation. We found that H O vapor has the highest reactivity due to the spin interaction between H
O vapor has the highest reactivity due to the spin interaction between H O and GaN surfaces. The bond length between the Ga and N on the -c GaN surface was increased by OH attacking the back side of three-fold Ga atom. The chemisorption on the m-plane was dominant. The intense reactions of oxidation and Al
O and GaN surfaces. The bond length between the Ga and N on the -c GaN surface was increased by OH attacking the back side of three-fold Ga atom. The chemisorption on the m-plane was dominant. The intense reactions of oxidation and Al Ga
Ga N formation for p-GaN were observed at the interface of the Al
N formation for p-GaN were observed at the interface of the Al O
O layer deposited by ALD using H
layer deposited by ALD using H O vapor. This study suggests that an oxidant gas other than H
O vapor. This study suggests that an oxidant gas other than H O and O
O and O should be used to avoid unintentional oxidation during Al
should be used to avoid unintentional oxidation during Al Ga
Ga N atomi layer deposition.
N atomi layer deposition.
Yoshigoe, Akitaka
Hoshako Riyo No Tebiki, p.130 - 138, 2019/02
The educational book on next-generation synchrotron radiation usage is partially written. This book is being planned by several professors at Tohoku University. In this book, the contents which have already reported in our recent paper [Appl. Phys. Lett. 112 (2018) 021603.] are mainly written. The future perspective on photoemission electron microscopy using next generation synchrotron radiation and its possibility to analyze environmental samples and insulating functional materials are also described.
Mekaru, Harutaka*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Nakamura, Michihiro*; Doura, Tomohiro*; Tamanoi, Fuyuhiko*
ACS Applied Nano Materials (Internet), 2(1), p.479 - 488, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:40 Percentile:83.26(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Organosilica nanoparticles are attractive for use as drug delivery systems for cancer therapy. Ideally, the nanoparticles need to degrade in the body after drug delivery to minimize their risk. However, the biodegradation of organosilica nanoparticles has not been thoroughly investigated. In this study, we used X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and field-emission scanning electron microscopy to investigate the degradation of organosilica nanoparticles by glutathione, a peptide found in cells. Our results indirectly indicate that glutathione is able to reduce the disulfide bonds present in the network of one type of the nanoparticles, promoting dissociation of these nanoparticles. The dissociated nanoparticles form large maple leaf-shaped structures under certain conditions. We consider the formation mechanism of these symmetrical structures.
Kobata, Masaaki; Okane, Tetsuo; Kobayashi, Keisuke*
Bunko Kenkyu, 67(4), p.161 - 162, 2018/08
We introduce hard X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, which has been rapidly introduced and developed in synchrotron radiation facilities. In particular, in order to realize electronic state analysis by hard X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy of insulators, the developed charge neutralization method was described. As an example, we showed adsorption behavior of cesium to nuclear reactor structure assuming Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. Finally, future prospects of hard X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy will be described.
Yamada, Takahiro*; Watanabe, Kenta*; Nozaki, Mikito*; Shih, H.-A.*; Nakazawa, Satoshi*; Anda, Yoshiharu*; Ueda, Tetsuzo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Hosoi, Takuji*; Shimura, Takayoshi*; et al.
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 57(6S3), p.06KA07_1 - 06KA07_6, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:29.69(Physics, Applied)Thermal oxidation of AlGaN surface and its impact on the electrical properties of AlGaN/GaN MOS capacitors were investigated by means of synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy (SR-PES), atomic force microscopy (AFM) and C-V measurements. SR-PES analysis revealed that the AlGaN surface is oxidized even at low temperature of 400 C, in contrast to no oxide formation on GaN surface. However, since no noticeable change in the surface morphology was observed at temperatures up to 800
C, in contrast to no oxide formation on GaN surface. However, since no noticeable change in the surface morphology was observed at temperatures up to 800 C, it can be concluded that an ultrathin oxide overlayer is formed on the AlGaN surface. On the other hand, for the oxidation treatments above 850
C, it can be concluded that an ultrathin oxide overlayer is formed on the AlGaN surface. On the other hand, for the oxidation treatments above 850 C, the formation of small oxide grains was observed over the entire area of the AlGaN surface, and the growth of oxide grains significantly degraded the surface morphology. Therefore, the AlGaN/GaN MOS capacitors were fabricated on the AlGaN surface oxidized at moderate temperatures up to 800
C, the formation of small oxide grains was observed over the entire area of the AlGaN surface, and the growth of oxide grains significantly degraded the surface morphology. Therefore, the AlGaN/GaN MOS capacitors were fabricated on the AlGaN surface oxidized at moderate temperatures up to 800 C. While we have confirmed that relatively good interface properties are obtained for direct AlON deposition without oxidation treatment, it was found that the oxidation treatment at 400
C. While we have confirmed that relatively good interface properties are obtained for direct AlON deposition without oxidation treatment, it was found that the oxidation treatment at 400 C leads to further improvement of interface properties and reduction of C-V hysteresis.
C leads to further improvement of interface properties and reduction of C-V hysteresis.
 /AlON stacked gate dielectrics for AlGaN/GaN MOS heterojunction field-effect transistors
/AlON stacked gate dielectrics for AlGaN/GaN MOS heterojunction field-effect transistorsWatanabe, Kenta*; Terashima, Daiki*; Nozaki, Mikito*; Yamada, Takahiro*; Nakazawa, Satoshi*; Ishida, Masahiro*; Anda, Yoshiharu*; Ueda, Tetsuzo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Hosoi, Takuji*; et al.
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 57(6S3), p.06KA03_1 - 06KA03_6, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:45.49(Physics, Applied)The advantage of SiO /AlON stacked gate dielectrics over SiO
/AlON stacked gate dielectrics over SiO , AlON and Al
, AlON and Al O
O single dielectric layers was demonstrated. Our systematic research revealed that the optimized stacked structure with 3.3-nm-thick AlON interlayer is beneficial in terms of superior interface quality, reduced gate leakage current and C-V hysteresis for next-generation high frequency and high power AlGaN/GaN MOS-HFETs.
single dielectric layers was demonstrated. Our systematic research revealed that the optimized stacked structure with 3.3-nm-thick AlON interlayer is beneficial in terms of superior interface quality, reduced gate leakage current and C-V hysteresis for next-generation high frequency and high power AlGaN/GaN MOS-HFETs.
Nozaki, Mikito*; Watanabe, Kenta*; Yamada, Takahiro*; Shih, H.-A.*; Nakazawa, Satoshi*; Anda, Yoshiharu*; Ueda, Tetsuzo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Hosoi, Takuji*; Shimura, Takayoshi*; et al.
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 57(6S3), p.06KA02_1 - 06KA02_7, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:66.85(Physics, Applied)We fabricated AlON dielectric films by repeating thin AlN deposition and in situ O oxidation for AlGaN/GaN MOS-HFETs. Uniform nitrogen distribution is achievable by the proposed ALD-based process and that nitrogen concentration can be precisely controlled by changing AlN thickness (ALD cycle number) in each step. It was found that AlON films grown by ALD system offers significant advantages in terms of practical application while keeping superior Vth stability and electrical properties at the insulator/AlGaN interface in AlGaN/GaN MOS-HFETs.
oxidation for AlGaN/GaN MOS-HFETs. Uniform nitrogen distribution is achievable by the proposed ALD-based process and that nitrogen concentration can be precisely controlled by changing AlN thickness (ALD cycle number) in each step. It was found that AlON films grown by ALD system offers significant advantages in terms of practical application while keeping superior Vth stability and electrical properties at the insulator/AlGaN interface in AlGaN/GaN MOS-HFETs.
 /GaN stacks for high-quality GaN-based metal-oxide-semiconductor devices with improved gate dielectric reliability
/GaN stacks for high-quality GaN-based metal-oxide-semiconductor devices with improved gate dielectric reliabilityYamada, Takahiro*; Watanabe, Kenta*; Nozaki, Mikito*; Yamada, Hisashi*; Takahashi, Tokio*; Shimizu, Mitsuaki*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Hosoi, Takuji*; Shimura, Takayoshi*; Watanabe, Heiji*
Applied Physics Express, 11(1), p.015701_1 - 015701_4, 2018/01
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:84.61(Physics, Applied)A simple and feasible method for fabricating high-quality and highly reliable GaN-based metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) devices was developed on the basis of systematic physical and electrical characterizations. Chemical vapor deposition of SiO films directly onto GaN substrates forming Ga-oxide interlayers was used to fabricate SiO
films directly onto GaN substrates forming Ga-oxide interlayers was used to fabricate SiO /GaO
/GaO /GaN stacked structures. Although well-behaved hysteresis-free GaN-MOS capacitors with extremely low interface state density below 10
/GaN stacked structures. Although well-behaved hysteresis-free GaN-MOS capacitors with extremely low interface state density below 10 cm
cm eV
eV were obtained by post-deposition annealing, Ga diffusion into overlying SiO
were obtained by post-deposition annealing, Ga diffusion into overlying SiO layers severely degraded the insulating property and dielectric breakdown characteristics of the MOS devices. However, this problem was found to be solved by employing rapid thermal processing, leading to superior performance of the GaN-MOS devices in terms of interface quality, insulating property and gate dielectric reliability.
layers severely degraded the insulating property and dielectric breakdown characteristics of the MOS devices. However, this problem was found to be solved by employing rapid thermal processing, leading to superior performance of the GaN-MOS devices in terms of interface quality, insulating property and gate dielectric reliability.
Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Kobayashi, Toru; Shimoyama, Iwao; Matsumura, Daiju; Tsuji, Takuya; Nishihata, Yasuo; Kogure, Toshihiro*; Okochi, Takuo*; Yasui, Akira*; et al.
Applied Physics Letters, 112(2), p.021603_1 - 021603_5, 2018/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:29.69(Physics, Applied)A synchrotron radiation photoemission electron microscope (SR-PEEM) was applied to demonstrate pinpoint analysis of micrometer-sized weathered biotite clay particles with artificially adsorbed cesium (Cs) atoms. Despite the insulating properties of the clay, we observed the spatial distributions of constituent elements (Si, Al, Cs, Mg, Fe) without charging issues. We found that Cs atoms were likely to be adsorbed evenly over the entire particle. Spatially-resolved X-ray absorption spectra (XAS) of the Cs M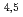 -edge region showed Cs to be present in a monocation state (Cs
-edge region showed Cs to be present in a monocation state (Cs ). Further pinpoint XAS measurements were also performed at the Fe L
). Further pinpoint XAS measurements were also performed at the Fe L -edge to determine the chemical valence of the Fe atoms. Our results demonstrate the utility of SR-PEEM as a tool for spatially-resolved chemical analyses of various environmental substances, which is not limited by the poor conductivity of samples.
-edge to determine the chemical valence of the Fe atoms. Our results demonstrate the utility of SR-PEEM as a tool for spatially-resolved chemical analyses of various environmental substances, which is not limited by the poor conductivity of samples.
 /GaN and its effect on electrical properties
/GaN and its effect on electrical propertiesYamada, Takahiro*; Watanabe, Kenta*; Nozaki, Mikito*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Hosoi, Takuji*; Shimura, Takayoshi*; Watanabe, Heiji*
no journal, ,
Formation of thin GaOx interlayer by thermal oxidation of SiO /GaN structure was investigated by spectroscopic ellipsometry and synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy. In the SiO
/GaN structure was investigated by spectroscopic ellipsometry and synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy. In the SiO /GaN structure before thermal oxidation, GaOx interlayer (about 4 nm) was already formed. This is considered to be attributable to O
/GaN structure before thermal oxidation, GaOx interlayer (about 4 nm) was already formed. This is considered to be attributable to O plasma exposure to GaN surface during SiO
plasma exposure to GaN surface during SiO deposition by plasma CVD. Thickness of the GaOx interlayer slightly increased about 1 nm by thermal oxidation up to 1000 degrees. This behavior indicates that the oxidation of GaN surface was markedly suppressed by the SiO
deposition by plasma CVD. Thickness of the GaOx interlayer slightly increased about 1 nm by thermal oxidation up to 1000 degrees. This behavior indicates that the oxidation of GaN surface was markedly suppressed by the SiO capping layer. C-V characteristics of SiO
capping layer. C-V characteristics of SiO /GaOx/GaN MOS capacitor with the thin GaOx layer, except that prepared at 1000 degrees, exhibited low frequency dispersion and hysteresis of below 10 mV. The measured C-V curves also well agreed with ideal C-V curves. These results demonstrate that the excellent GaN MOS interface properties were realized by the insertion of thin GaOx interlayer.
/GaOx/GaN MOS capacitor with the thin GaOx layer, except that prepared at 1000 degrees, exhibited low frequency dispersion and hysteresis of below 10 mV. The measured C-V curves also well agreed with ideal C-V curves. These results demonstrate that the excellent GaN MOS interface properties were realized by the insertion of thin GaOx interlayer.
Watanabe, Kenta*; Nozaki, Mikito*; Yamada, Takahiro*; Nakazawa, Satoshi*; Anda, Yoshiharu*; Ishida, Masahiro*; Ueda, Tetsuzo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Hosoi, Takuji*; Shimura, Takayoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
AlGaN/GaN HFET has gained much attention as next-generation high frequency and high power devices. Among various insulating materials, Al O
O is one of the potential candidates. However, large amount of electrical defects at MOS interfaces severely degrade both drive current and threshold voltage stability. Positive Vth shift due to electron trapping in Al
is one of the potential candidates. However, large amount of electrical defects at MOS interfaces severely degrade both drive current and threshold voltage stability. Positive Vth shift due to electron trapping in Al O
O layer by applying positive gate bias is often observed for Al
layer by applying positive gate bias is often observed for Al O
O /AlGaN/GaN MOS structures. We have recently reported that N incorporation into Al
/AlGaN/GaN MOS structures. We have recently reported that N incorporation into Al O
O significantly reduces electron traps in Al
significantly reduces electron traps in Al O
O layer for Si and SiC MOS devices. In this study, we systematically investigated the interface reaction between Al-based dielectrics (Al
layer for Si and SiC MOS devices. In this study, we systematically investigated the interface reaction between Al-based dielectrics (Al O
O and AlON) and AlGaN layer during deposition and post-deposition annealing (PDA), and revealed high thermal stability of AlON/AlGaN interface.
and AlON) and AlGaN layer during deposition and post-deposition annealing (PDA), and revealed high thermal stability of AlON/AlGaN interface.
Yoshigoe, Akitaka
no journal, ,
Decontamination of Cs trapped in clays is considered to be difficult because Cs atoms tightly bind to the clays. Therefore, the development of the methods to efficiently remove Cs from polluted areas has become a matter of great importance and has motivated research into basic understanding Cs adsorption to clay and its physicochemical properties. In this study, a synchrotron radiation photoemission electron microscope (SR-PEEM) was applied to demonstrate pinpoint analysis of micrometer-sized weathered biotite clay particles with artificially adsorbed non-radioactive Cs. Despite the insulating properties of the clay, we observed the spatial distributions of constituent elements with nanometer resolution without charging issues through a proper surface treatment. Pinpoint XAS spectra indicated the chemical states of Fe and Cs. The results strongly suggest that Cs adsorption took place via electrical charge compensation mechanisms. Further technical developments are required to apply to real-world samples with extremely low Cs content; however, we succeeded the first step towards applying this method to nanoscale analysis of Cs-adsorbed clay minerals.
Yoshigoe, Akitaka
no journal, ,
In this conference on surface science, the results of pinpoint analysis of clay minerals artificially containing Cs using synchrotron radiation photoemission electron microscopy are talked as an invited lecture. Nano-scaled realspace analysis of distribution maps of the constituent elements and chemical states of both Cs and Fe atoms are described to discuss the model of Cs adsorption into clay minerals. Future perspective of the application of synchrotron radiation photoemission electron microscopy to various kinds of research fields are also talked.
Kobata, Masaaki; Satou, Yukihiko; Okane, Tetsuo; Kawasaki, Ikuto; Yoshii, Kenji; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Osaka, Masahiko; Owada, Kenji*
no journal, ,
In order to enable chemical state analysis by hard X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (HAXPES) for environmental samples such as radioactive microparticles collected around Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, charge neutralization technique established using ion and electron coaxial irradiation. Using this technique, the chemical state analysis of the radioactive microparticles was realized.
Kakiuchi, Takuhiro*; Anai, Ryota*; Saiki, Taiju*; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
no journal, ,
Initial oxidation mechanism of hafnium adsorbed Si(111)-7 7 [Hf-Si(111), the thickness of Hf:0.5 monolayer] was studied by synchrotron radiation X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The individual Hf atoms were associated with the back bonds of Si rest atoms or Si adatoms on Si(111)-7
7 [Hf-Si(111), the thickness of Hf:0.5 monolayer] was studied by synchrotron radiation X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The individual Hf atoms were associated with the back bonds of Si rest atoms or Si adatoms on Si(111)-7 7, and the Hf monosilicide HfSi) unit was formed on the outermost surface. Following the HfSi units immediately reacted with the thermal O
7, and the Hf monosilicide HfSi) unit was formed on the outermost surface. Following the HfSi units immediately reacted with the thermal O molecules [translational energy (Et=0.03eV], Hf silicates (Hf-O-Si) were produced. In addition, some dissociated O atoms were inserted between the adsorbed Hf atoms. As a result, Hf sub-oxides/silicates up to 3+ states were formed. When a non-equilibrium condition was induced by irradiation of the supersonic O
molecules [translational energy (Et=0.03eV], Hf silicates (Hf-O-Si) were produced. In addition, some dissociated O atoms were inserted between the adsorbed Hf atoms. As a result, Hf sub-oxides/silicates up to 3+ states were formed. When a non-equilibrium condition was induced by irradiation of the supersonic O molecular beam of Et = 0.39 eV, the Hf4+ state was confirmed along with and the oxidation of Si bulk. This indicates that there is an activation energy to oxidize the Hf-Si bonds of the bulk side.
molecular beam of Et = 0.39 eV, the Hf4+ state was confirmed along with and the oxidation of Si bulk. This indicates that there is an activation energy to oxidize the Hf-Si bonds of the bulk side.